Together
in Transplant
Advancing Care
Through Innovation
Discover the solutions from CareDx designed to empower clinicians and improve patient outcomes.
Molecular rejection is an active, dynamic process
Rejection begins before clinical signs and symptoms can be observed. Molecular rejection testing can reveal it.
Traditional tools don't fully address the dynamic nature of rejection
Molecular rejection is an active, dynamic process
Rejection begins before clinical signs and symptoms can be observed. Molecular rejection testing can reveal it.
Natural Progression of Rejection
That Could Lead to Graft Loss1
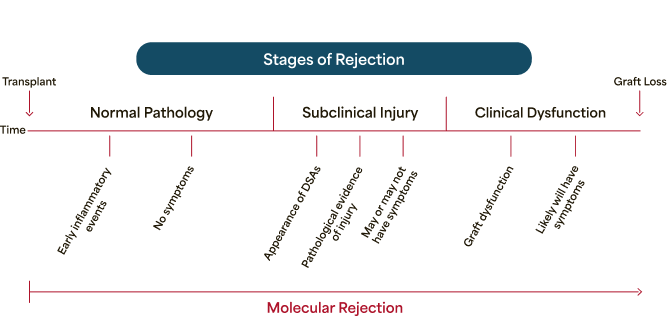
(Pinch to zoom)
Traditional tools don't fully address the dynamic nature of rejection.
The only molecular rejection test that measures both immune activation and graft injury
The intersection of immune activation and graft injury reveals risk strata not seen with either test alone.
- Extensively validated in multicenter prospective studies
- 2,732 patients across 67 transplant centers2
- Provides another dimension of risk compared with dd-cfDNA alone2,3
HeartCare: Clinically validated outcomes in a landmark multicenter registry
(Pinch to zoom)
The HeartCare Personalized Risk Report
HeartCare is the only test that provides a Personalized Risk Report, combining measures of immune activation and graft injury for more precise risk assessment.
(Pinch to zoom)
AlloMap(+) is ≥30 for ≥2-6 months or ≥34 for >6 months. AlloSure(+) is ≥0.2%.
This information is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. A physician's test selection and interpretation, diagnosis, and patient management decisions should be based on their education, clinical expertise, current guidelines, and assessment of the patient.
This information is designed for the context of surveillance testing for ACR; For patients that are at risk of ABMR or being tested in other clinical context, different guidance may apply.
ACR: acute cellular rejection; ABMR: antibody-mediated rejection; CMV: cytomegalovirus.
An AlloMap(+), AlloSure(+) result doubled risk of poor outcomes, even without histological rejection5
Cumulative Incidence of Poor
Outcomes in Patients Without
Rejection Between 2-6 Months
Post-transplant (N=1,748)5
Cumulative Incidence of Poor Outcomes in Patients Without
Rejection Between 2-6 Months Post-transplant (N=1,748)5

(Pinch to zoom)
AlloMap drives deeper insights alongside dd-cfDNA results5
AlloMap(+), along with
AlloSure(+), reveals a high-risk
group, even in the absence of
rejection or graft dysfunction
AlloMap(+), along with AlloSure(+), reveals a high-risk group, even in the absence of rejection or graft dysfunction
Cumulative Incidence of Poor
Outcomes in Patients Without
Rejection Between 2-6 Months
Post-transplant (N=1,748)5
Cumulative Incidence of Poor Outcomes in Patients Without
Rejection Between 2-6 Months Post-transplant (N=1,748)5

(Pinch to zoom)
Latest HeartCare data
Featured Webinar: Watch On Demand
Hear directly from leading experts as they discuss advancements in post-transplant care, including non-invasive molecular diagnostics, real-world examples, and validated results.

Ann Nguyen, MD
University of Chicago
Assistant Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Heart Transplant Program, University of Chicago Medicine
Nirav Raval, MD
BayCare Health System
Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiologist at BayCare Health System
New publication demonstrates that HeartCare helps identify higher-risk patients more precisely than histology or dd-cfDNA alone
ABMR: antibody-mediated rejection; ACR: acute cellular rejection; CMV: cytomegalovirus; dd-cfDNA: donor-derived cell-free DNA; EMB: endomyocardial biopsy; IQR: interquartile range.
Detect the early signs of molecular rejection
AlloSure is a robust predictor of severity of rejection, with multiple thresholds for a more precise risk assessment6-8

Relative change value (RCV) compares sequential tests to identify the percentage difference between them.
Detect the early signs of molecular rejection
AlloSure is a robust predictor of severity of rejection, with multiple thresholds for a more precise risk assessment6-8

Relative change value (RCV) compares sequential tests to identify the percentage difference between them.
There is a strong correlation between AlloSure levels and MVI
AlloSure may identify patients who do not fit the criteria for AMR but may have significant underlying injury10
MVI, DSA-negative and C4d-negative, has been recognized as a distinct rejection phenotype according to Banff 2022 Classification.11 This is associated with a significant risk of graft failure.12
- dd-cfDNA (AlloSure Kidney) is currently the only test proven to help identify patients with MVI, DSA-, C4d-negative13
The ability to detect kidney injury, including MVI, starts at the 0.5% AlloSure level10
AlloSure Levels and Severity of MVI10

AMR: antibody-mediated rejection; C4d: complement component 4d; dd-cfDNA: donor-derived cell-free DNA; DSA: donor-specific antibodies; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; MVI: microvascular inflammation; NS: nonsignificant.
There is a strong correlation between AlloSure levels and MVI
AlloSure may identify patients who do not fit the criteria for AMR but may have significant underlying injury10
MVI, DSA-negative and C4d-negative, has been recognized as a distinct rejection phenotype according to Banff 2022 Classification.11 This is associated with a significant risk of graft failure.12
- dd-cfDNA (AlloSure Kidney) is currently the only test proven to help identify patients with MVI, DSA-, C4d-negative13
AMR: antibody-mediated rejection; C4d: complement component 4d; dd-cfDNA: donor-derived cell-free DNA; DSA: donor-specific antibodies; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; MVI: microvascular inflammation; NS: nonsignificant.
Elevate rejection detection with AlloSure Plus®
Powered by AlloSure to assess the probability of rejection with more precision6,9,10,14
AlloSure Plus is an automated, clinically validated risk prediction model that leverages AI technology to integrate AlloSure with traditional tools to provide a kidney transplant patient's personalized assessment of the probability of rejection.
Latest AlloSure Kidney data
AlloSure dd-cfDNA significantly improves rejection yield in kidney transplant biopsies
AMR: antibody-mediated rejection; C4d: complement component 4d; dd-cfDNA: donor-derived cell-free DNA; DSA: donor-specific antibodies; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; MVI: microvascular inflammation; NS: nonsignificant.
Connect With CareDx
Sign up for future webinars to stay in the know.
All fields are required.

References
1. Colvin MM, Cook JL, Chang P, et al. Antibody-mediated rejection in cardiac transplantation: emerging knowledge in diagnosis and management: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(18):1608-1639. 2. Khush K, Hall S, Kao A, et al. Surveillance with dual noninvasive testing for acute cellular rejection after heart transplantation: outcomes from the Surveillance HeartCare Outcomes Registry. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2024;43(9):1409-1421. 3. Uriel N, Hall S, Sayer G, et al. Abnormal dual molecular testing confers risk even with a negative biopsy after heart transplantation [abstract]. Presented at the ISHLT 45th Annual Meeting and Scientific Session; April 27–30, 2025. Boston, MA. Pub #240. 4. Henricksen E, Khush K, Intrieri T, et al. Less is more: 5-year outcomes after adoption of early dual non-invasive monitoring after heart transplant. Presented at the ISHLT 45th Annual Meeting and Scientific Session; April 27–30, 2025. Boston, MA. Pub #268. 5. Data on file. CareDx; 2025. 6. Aubert O, Ursule-Dufait C, Brousse R, et al. Cell-free DNA for the detection of kidney allograft rejection. Nat Med. 2024;30(8):2320-2327. 7. Bloom RD, Bromberg JS, Poggio ED, et al. Cell-free DNA and active rejection in kidney allografts. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(7):2221-2232. 8. Stites E, Kumar D, Olaitan O, et al. High levels of dd-cfDNA identify patients with TCMR 1A and borderline allograft rejection at elevated risk of graft injury. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(9):2491-2498. 9. Bromberg JS, Brennan DC, Poggio E, et al. Biological variation of donor-derived cell-free DNA in renal transplant recipients: clinical implications. J Appl Lab Med. 2017;2(3):309-321. 10. Bu L, Gupta G, Pai A, et al. Clinical outcomes from the Assessing Donor-derived cell-free DNA Monitoring Insights of kidney Allografts with Longitudinal surveillance (ADMIRAL) study. Kidney Int. 2022;101(4):793-803. 11. Naesens M, Roufosse C, Haas M, et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Report: reappraisal of microvascular inflammation and the role of biopsy-based transcript diagnostics. Am J Transplant. 2024;24(3):338-349. 12. Sablik M, Sannier A, Raynaud M, et al. Microvascular inflammation of kidney allografts and clinical outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2025;392(8):763-776. 13. Sablik M, Brousse R, Recape M, et al. Association of donor-derived cell-free DNA with microvascular inflammation phenotypes in kidney allografts. Presented at: ESOT Congress; June 29-July 2, 2025; London, UK. 14. Oral WTC presentation by Dr. Romain Brousse on August 5, 2025 (assessing performance of AlloSure Plus without DSA); CareDx data on file.



